Humidity Risks for Your HVAC and Indoor Air Quality
Humidity does more than make a summer day uncomfortable. Inside your home, out-of-balance moisture levels can quietly wreak havoc on your heating and cooling system. Too much or too little humidity affects not only your HVAC equipment’s lifespan but also the health of everyone inside your walls. It can trigger allergies, ruin flooring, and lead to higher energy bills month after month. Knowing how humidity damage begins and what to do about it puts you in control of your comfort, well-being, and money. This article reveals the hidden dangers humidity poses to your system, your indoor air quality, and your overall living environment. Learn proven ways for effective HVAC moisture control that protect your investment all year round.
How Humidity Influences Everyday Comfort and Health
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Indoors, this moisture level directly impacts how warm or cool a room feels and how easily the body can regulate temperature. Excess moisture creates an environment where sweat cannot evaporate efficiently, causing rooms to feel stuffy and clammy. Low humidity allows sweat to evaporate too quickly, making rooms feel chilly even if the thermostat shows a comfortable number.
It does not stop at temperature perception. High or low indoor moisture shapes air quality, determines how dust and allergens move, and affects how much you spend on utilities each month. Households with balanced humidity notice fewer respiratory complaints, smoother skin, and less static electricity. Those with unaddressed humidity swings often deal with health complaints, shifting woodwork, peeling paint, and a host of HVAC system failures.
Humidity sources in the home include cooking, showering, laundry, indoor plants, and even breathing. Excessively sealed homes may retain too much moisture in certain seasons or, with constant cooling or heating, lose necessary humidity in others. The consequences ripple through every room, impacting air quality in ways even frequent cleaning cannot fully offset.
High Humidity: The Silent Strain on HVAC Systems
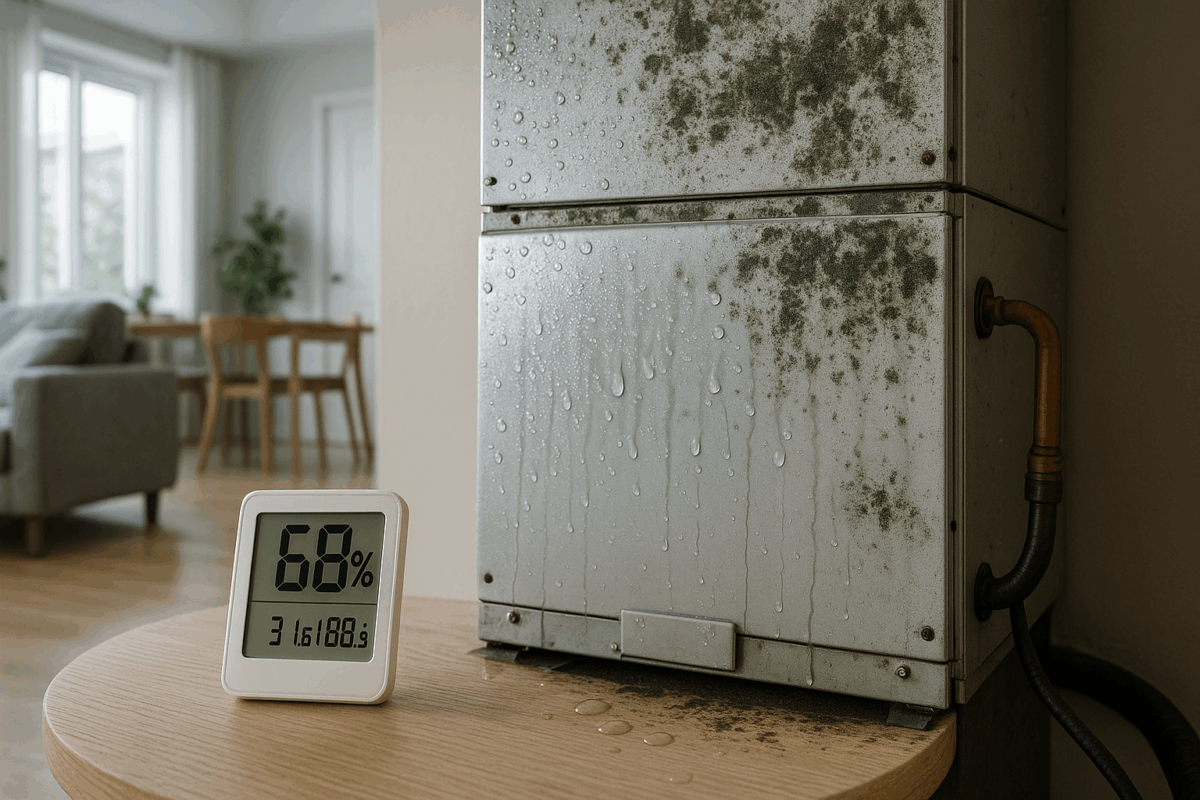
Air conditioners do more than cool air. Their refrigerant coils also remove water vapor, often called “latent heat”, from indoor air as a natural byproduct. When humidity rises above the ideal range, the workload on these systems grows sharply. Your system operates in longer cycles or short cycles, continually turning off and on. These constant starts and stops decrease the lifespan of compressors, fans, and motors.
High humidity can overwhelm the evaporator coil, leaving condensation to build up and not drain correctly. Persistent moisture can corrode metal components and cause electrical failures. The proliferation of water in ducts and internal chambers attracts dust mites and other allergens. Moisture-laden air also clings to finer particles, pushing them deeper into filters and clogging the airways that keep airflow strong.
Power consumption rises quickly when humidity stays unchecked. Your air conditioner must work harder to reach your desired temperature, increasing electrical loads and sending bills higher every month. You get less cool, less comfort, and a higher risk that key components will need untimely repair or replacement. In humid areas or summers, this effect can cut years from your system’s useful lifespan.
When Humidity Fuels the Growth of Mold and Allergens
Excess moisture in the air can ignite a rapid takeover of mold, mildew, and dust mites. These thrive in conditions above 50 percent relative humidity. Hidden colonies set up in ductwork, behind drywall, under carpets, and around windows where condensation lingers. Invisible spores migrate through your HVAC system, lowering indoor air quality and leading to problems that surface months or even years later.
Mold and mildew do not only produce a musty odor. They release airborne particles that can worsen asthma, trigger respiratory infections, and fuel allergic reactions. People with weakened immune systems or young children may face more severe symptoms. Mold spores are notoriously tough to remove once established. Air filters can trap some, but persistent humidity ensures their return unless the air is dried out.
HVAC ducts are particularly susceptible to hidden contamination, turning what should be the lungs of your home into distribution zones for irritants. Long-term exposure can also damage the system itself, eroding insulation and contributing to rust or pitting of metal ducts. Preventing excessive moisture is more cost-effective than any after-the-fact mold remediation could ever be.
Damage to Woodwork, Paint, and Home Structure
Moisture that hangs in the air for weeks or months infiltrates more than just your HVAC. Hardwood floors begin to cup, warp, or buckle. Door frames and windows swell, causing them to stick or lose their precise fit. Joints in cabinetry or wood trim crack. The very structure of the home can move as fasteners rust and framing materials lose their intended shape.
Paint, wallpaper, and finishes lift or bubble as the adhesive breaks down under persistent moisture. Even stone materials are not immune, as grout and caulking may develop mildew or begin to crumble. Repairs for these issues range from cosmetic touch-ups to costly floor or wall replacements, often coming as a surprise until damage is severe.
Fixing swollen doors, warped flooring, or peeling paint generally requires strict moisture control to prevent recurrence. This makes managing humidity at the system level one of the most effective long-term strategies for keeping your home intact and beautiful.
Low Humidity Challenges: Dry Air and Comfort Loss
Dry air can be just as damaging as excess moisture. Low indoor humidity is common during cold months when heating systems run frequently, especially in homes with older, tightly sealed windows. This leads to uncomfortable dry skin, chapped lips, scratchy noses, and irritated eyes. Static electricity builds up on clothing and carpets, creating small shocks and potentially harming sensitive electronics.
Furniture and wood floors tell the story in another way. With not enough moisture, wood dries out, leading to gapping between planks, separation of wood joints, or outright cracking. Book bindings, photographs, and musical instruments can shrink or warp, decreasing functional and sentimental value alike.
Children and those with allergies may experience higher rates of nosebleeds, coughs, or dry coughs that coincide with low humidity seasons. The home feels colder, often leading to a thermostat set several degrees higher just to feel normal. This drives up heating bills, while not resolving the underlying discomfort caused by a lack of moisture in the air.
Energy Waste: How Humidity Ups Your Bills
Comfort is not the only casualty when humidity levels fall outside of the 30 to 50 percent sweet spot. A humid house in summer means your air conditioner keeps fighting a losing battle, running longer than need be and sometimes never reaching its thermostat target. In winter, dry air allows heat to slip away faster. It leads to constant furnace or heat pump operation for the same reason.
Bills can climb significantly as your heating or cooling system burns more electricity or gas trying to regain balance. These expenses often go unnoticed month by month but add up annually to much more than what humidity management would cost. This cycle also shortens the lifespan of critical HVAC parts, raises the risk of short cycling, and increases the chance of breakdowns that require costly emergency service.
Investing in balanced humidity reduces both peaks and valleys in your energy usage. It provides you more steady, predictable comfort and puts money back in your pocket over the long haul.
Recognizing the Signs of Humidity Problems
Homeowners who know what to look for can quickly spot the effects of poor humidity control. Persistent condensation on windows is a classic sign of excess moisture. Sticky or musty odors in closets, attics, or basements may signal both humidity and mold runs atop the problem. Anyone who notices growth behind furniture or bending woodwork should suspect out-of-balance indoor air.
Cracking paint, frequent static shocks, and gapping floorboards point to humidity levels that are too low. Changes in how doors or windows fit, along with coughs or increased allergy symptoms, should also prompt a second look at air moisture readings throughout the home.
HVAC systems themselves offer signals. Unusual noises, short cycling, frequent blower runs, or inconsistent cooling suggest the system is reacting to invisible, ongoing humidity problems. Catching these issues early can be the difference between a simple fix and a major renovation.
Humidity Damage: Why Prevention Beats Repairs
Once moisture imbalances take root, the damage can be staggering. Mold remediation, duct replacement, and flooring repair all cost far more than establishing proper HVAC moisture control in the first place. Some problems, like hidden mold, may remain invisible until health complications force expensive interventions.
Dealing with the aftermath will often mean living with reduced indoor air quality and recurring repairs for years to come. Whole systems can become so compromised that full replacements are necessary. Preventative steps not only keep your current equipment running longer but also protect your investment in every aspect of your home’s interior.
Poor humidity management can void system warranties. Neglected maintenance often gives manufacturers a way to deny claims, leaving you shouldering expenses alone. The upfront effort to maintain correct moisture is minor compared to the headaches and bills of system restoration or replacement.
Proven Ways to Measure Indoor Humidity
Controlling humidity begins with knowing where your space stands. Hygrometers are simple devices, available as digital or analog sensors, that give real-time readings of indoor moisture. Place them in living areas and in rooms that tend to run humid, such as bathrooms, kitchens, or basements. Readings between 30 and 50 percent indicate healthy air. Above or below that threshold, it is time to act.
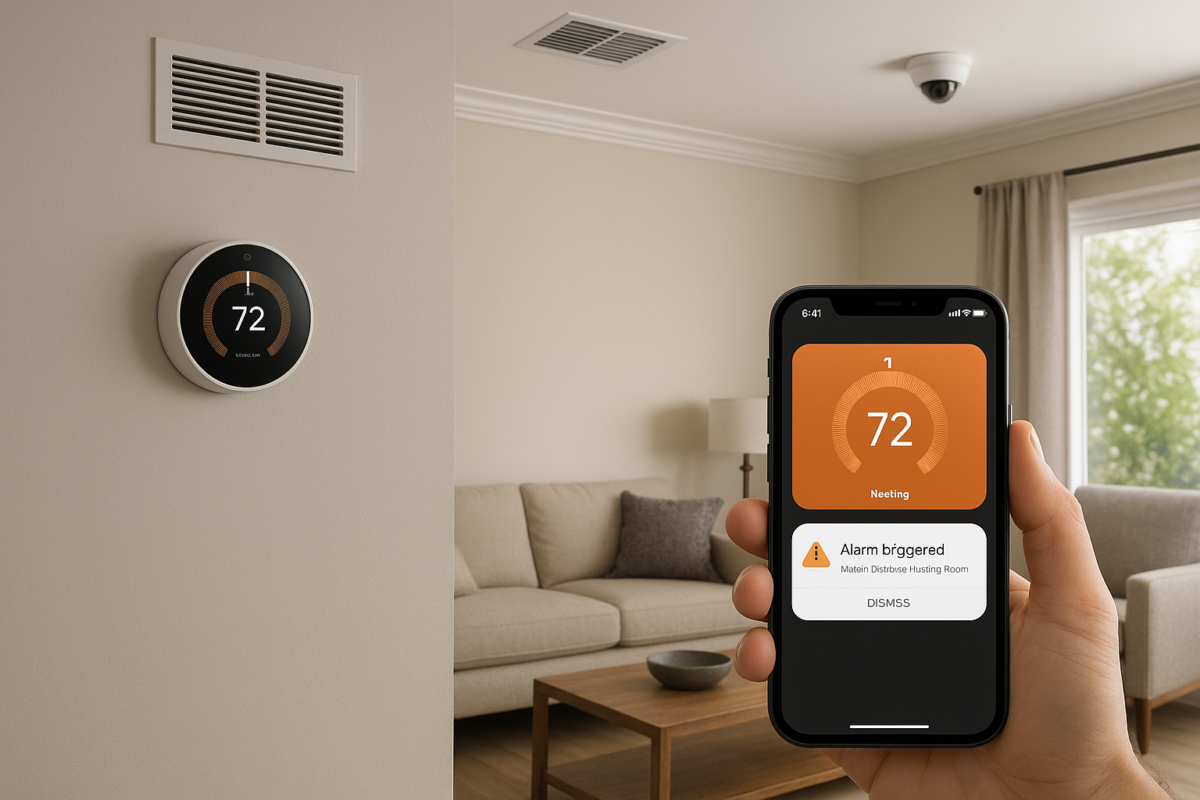
Smart thermostats and home automation systems often integrate humidity sensors. These allow for tracking trends over weeks or months and can even trigger automated adjustments using dehumidifiers, humidifiers, or ventilation systems. Accurate measurement takes away guesswork and makes solutions more targeted and effective.
Do not rely just on window condensation or discomfort as warning signs. True control begins with hard numbers. Invest in quality sensors that withstand seasonal changes and connect with your other air management equipment if possible. This is your first tool for defending both your system and your health.
Smart Strategies for HVAC Moisture Control
Correcting humidity problems combines active equipment, sound building practices, and regular system care. In areas with persistent moisture, using a dehumidifier, either portable or whole-home, unbinds your cooling system from double-duty work. For spaces that dry out, humidifiers restore lost comfort and improve air quality all winter long.
Balance also means trapping excess moisture before it spreads. Use exhaust fans while bathing or cooking to send water vapor outside rather than into walls or air ducts. Make sure laundry rooms vent dryers properly, and consider plants that draw up water efficiently. Airtightness can be useful, but sometimes it takes a balanced approach. Overly sealed homes trap both pollutants and moisture, creating new challenges if not paired with the right equipment.
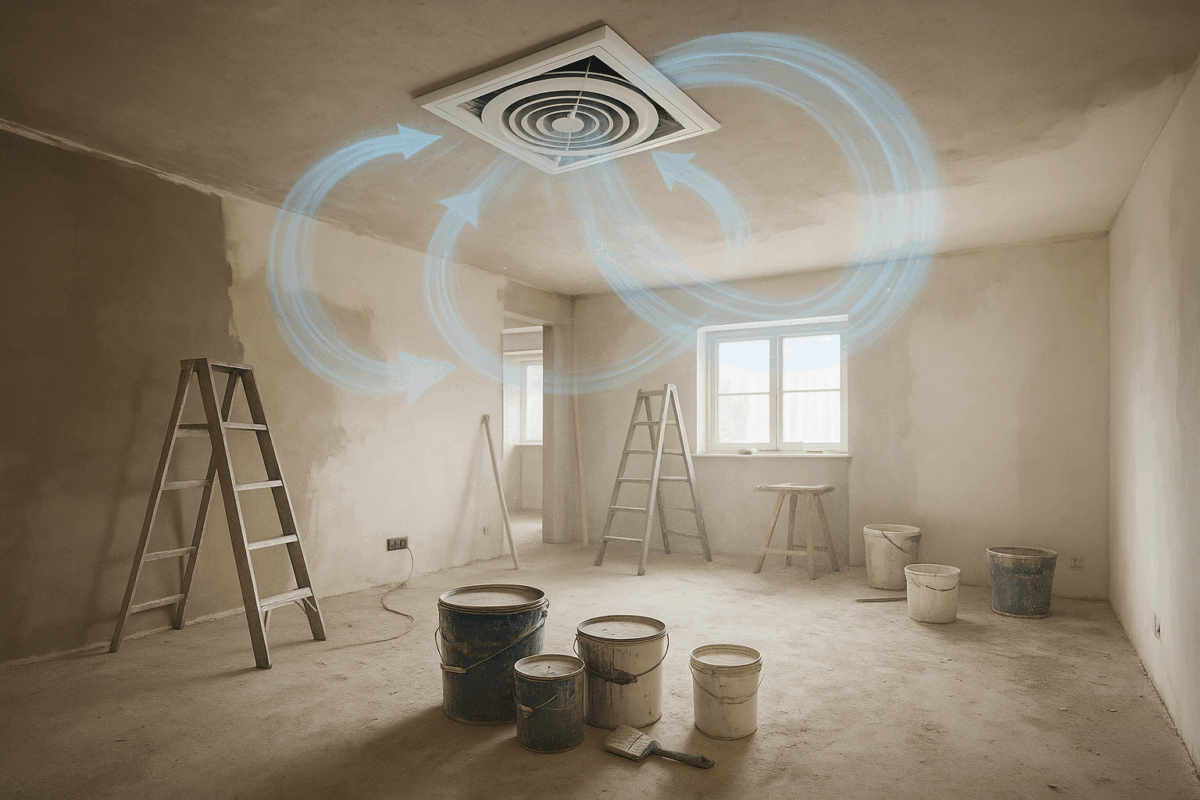
Whole-house ventilation systems like energy recovery ventilators automatically manage incoming and outgoing air, balancing seasonal needs across your entire home. These solutions adjust for temperature, pressure, and moisture, keeping your home within optimal humidity ranges year-round.
Routine HVAC Maintenance: Your Best Defense
Preventing humidity-related damage requires consistent attention to your heating and cooling system. Schedule regular professional maintenance at least twice per year. This involves cleaning condensate drains, inspecting for leaks, and changing or washing air filters. Blocked or dirty filters magnify humidity problems and force the system to run harder than necessary.
Inspect evaporator and condenser coils for cleanliness. Clean coils remove both heat and moisture with efficiency. Check that insulation in ducts has not become saturated or mildewed. Clear debris and look for rust or corrosion on metal parts. If there is any sign of standing water or persistent moisture inside equipment, address it before it leads to bigger issues.
Annual tune-ups identify early warning signs that might otherwise go unnoticed for years. A knowledgeable technician has the tools and experience to fine-tune your whole HVAC system for efficient performance and spot hidden risks of future humidity damage. Proactive care pays for itself in lower bills, fewer repairs, and greater peace of mind all season long.
Creating a Healthier, More Efficient Living Environment
Balancing humidity inside your home pays dividends in comfort, health, and efficiency. Taking action on humidity protects more than just your air conditioning or furnace. It defends flooring, surfaces, electronics, artwork, and even family heirlooms from warping or decay. Everyone benefits from cleaner air, fewer allergens, and less mold in everyday life.
Regular checkups and humidity monitoring keep your system running at its best. Modern equipment makes it easy to automate and fine-tune your indoor environment. Small steps, like using fans or setting up a smart thermostat, prevent moisture buildup before it affects comfort or causes expensive repairs. The reward is a home that feels consistently fresh every season.
Start with small changes, invest in yearly inspections, and stay ahead of humidity swings. Proven strategies for HVAC moisture control mean your system lasts longer, your air is easier to breathe, and your bills stay manageable. Never underestimate the hidden dangers of humidity. Taking charge now is the best way to protect your living space, your health, and your peace of mind.